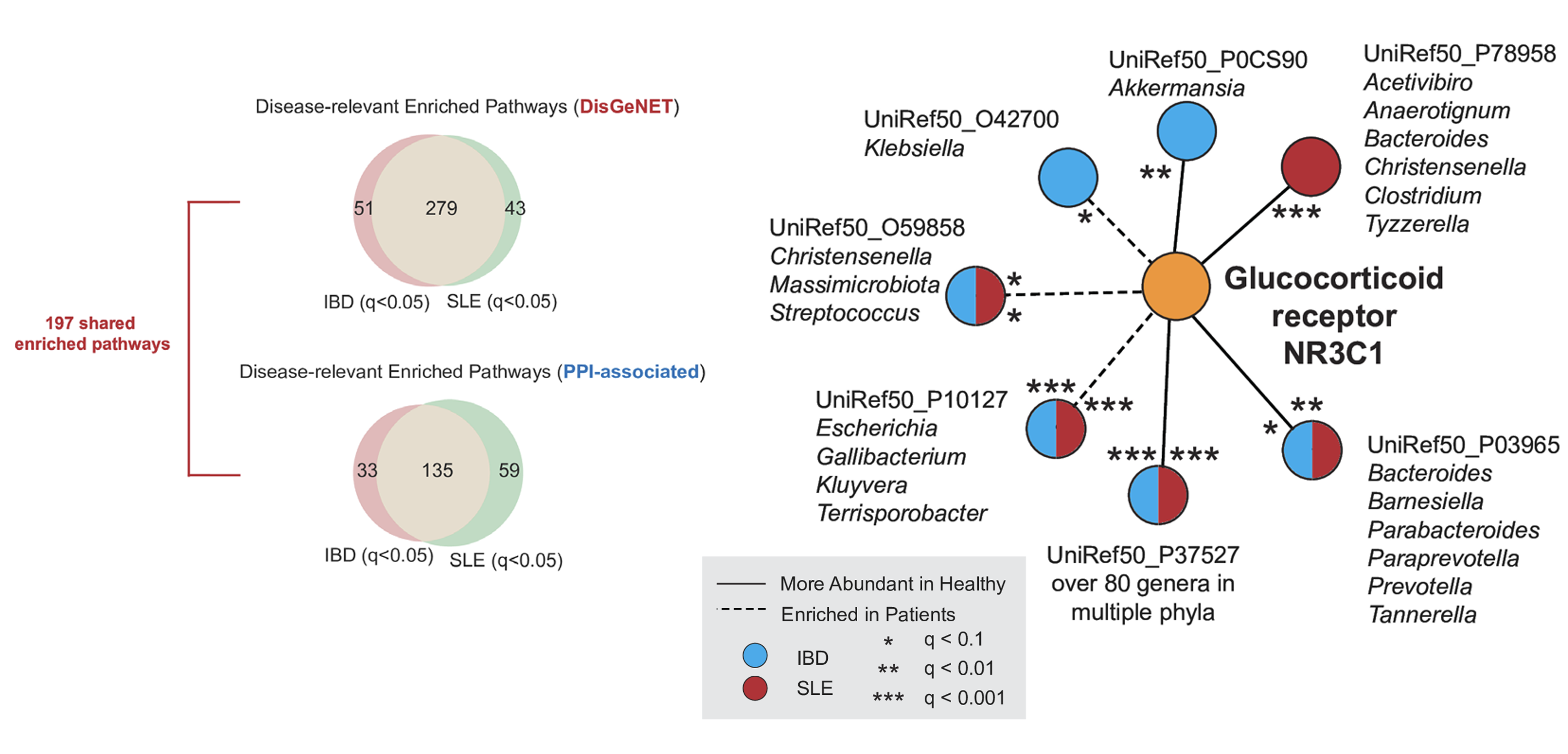
Shared microbiome features between systemic lupus erythematosus and inflammatory bowel disease
In our study, we explored the gut microbiome across several autoimmune diseases, focusing particularly on systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). We found that these two conditions share a strikingly similar set of microbial signatures distinct from other autoimmune disorders. These microbes may affect critical immune pathways, such as glucocorticoid signaling and interleukin-12, potentially disrupting the body’s natural immune response and fueling disease progression. By analyzing metagenomic data, we revealed that certain bacteria may interact with host proteins, which could influence immune system function!